In general decreased hybridization increases acidity because there is greater s character in the orbital containing the lone pair so it is held closer to the nucleus.
Why are vinylic hydrogens not acidic.
Other characteristics alkynes attached hydrogen have the formulas of h cc h or r cc h with r representing any alkyl group such as methyl ethyl etc.
Number of hydrogen atoms.
For example the following compounds have all been isolated from the volatile oil of chondrococcus hornemanni a red seaweed found in the pacific ocean.
Expert answer 100 2 ratings previous question next question get more help from chegg.
I m talking about the proton bonded to the carbonyl carbon not the alpha proton.
Vinylic carbon can have either two double bonds in its sides or one double bond.
Vinylic c h bond is lower.
Vinylic carbon can have only two carbon as the maximum number.
Allylic carbon can have a maximum of 3 hydrogen atoms.
Organohalogen compound organohalogen compound vinylic halides.
Get 1 1 help now from expert chemistry tutors.
Allylic carbon only forms a single bond.
Vinylic chlorides and bromides constitute a diverse class of marine natural products.
In line formulas such as the following a carbon atom is assumed to be at every.
Or halide attached to the carbon.
The gases are not toxic per se but can act to exclude oxygen in breathing zone during an incident.
Why is an aldehyde not acidic.
For example the acidic hydrogens in carboxylic acids come at higher chemical shifts than most other types of hydrogens since there is a lower electron density around them thus they are relatively deshielded.
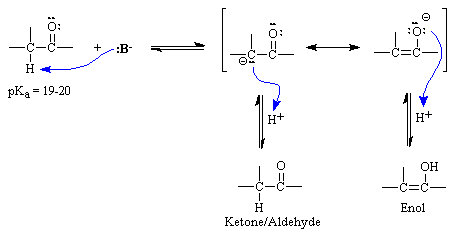
Tautomerism essentially requires the presence of α hydrogen the hydrogen atom present generally adjacent to the functional group or the hydrogen atom present on the carbon which is adjacent to the carbon attached to the functional group.
The first category of acids are the proton donors or brønsted lowry acids in the special case of aqueous solutions proton donors form the hydronium ion h 3 o and are known as arrhenius acids.
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of donating a proton hydrogen ion h a brønsted lowry acid or alternatively capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair a lewis acid.